Dr. Dhanish Parekh
MBBS, DNB, Mch Neurosurgery
Consultant Neurosurgeon
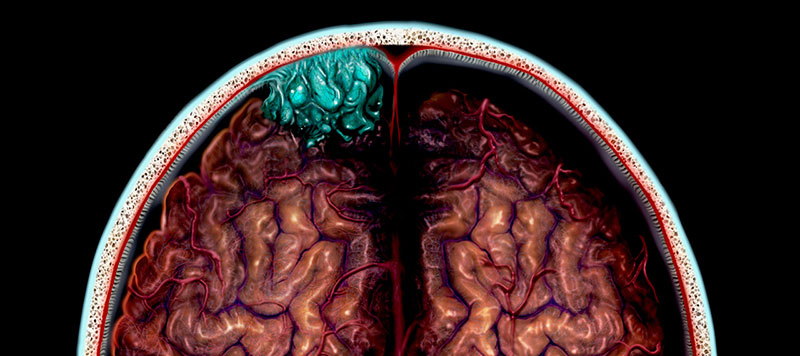
Brain tumors can occur in both adults and children, and while they share some similarities, there are key differences in their types, presentation, and treatment.
Headaches, seizures, changes in vision, difficulty speaking, weakness or numbness, personality changes.
MRI and CT scans are used to identify the tumor's location and type. A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the type and location of the tumor.
Headaches, nausea, vomiting (especially in the morning), balance problems, changes in behaviour, developmental delays, or seizures.
Similar to adults, using MRI or CT scans. A biopsy may be necessary for definitive diagnosis.
Often involves surgery, followed by radiation therapy and chemotherapy, especially for high-grade Tumors. The approach may be more conservative in very young children to avoid radiation exposure.
Brain Tumors in both adults and children present unique challenges, and understanding their specific characteristics is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment can improve outcomes for both populations.